When it comes to culinary delights, veal often takes center stage, but what exactly is it made from? This tender delicacy has sparked curiosity and debate among food lovers and chefs alike. Is it just a fancy word for baby cow? Well, sort of! Veal comes from young calves, typically under a year old, raised specifically for their tender meat.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Veal
Veal comes from young calves, typically aged between 6 to 12 months. This meat is prized for its tenderness and unique flavor, making it a sought-after ingredient in gourmet cooking. Calves raised for veal are often of specific breeds, such as Holstein or Jersey, and are fed a specialized diet to enhance the quality of the meat.
Different methods of veal production exist, including traditional and more modern approaches. Conventional veal production involves raising calves in group housing, allowing them some interaction with other animals. In contrast, certain types of veal, such as milk-fed veal, are raised in individual pens and fed a liquid diet to achieve a pale color and delicate texture.
The ethical considerations surrounding veal production often spark discussions among consumers. Critics highlight the concern over specific farming practices, while proponents argue for humane methods that prioritize animal welfare. These discussions can influence purchasing decisions and impact market demand.
Various types of veal are available, each catering to specific culinary needs. For example, cutlets, chops, and shanks provide a range of options for chefs. Some recipes call for braising, while others favor grilling or sautéing, showcasing veal’s versatility in the kitchen. Understanding these distinctions enhances the appreciation for veal as an ingredient.
Types of Veal
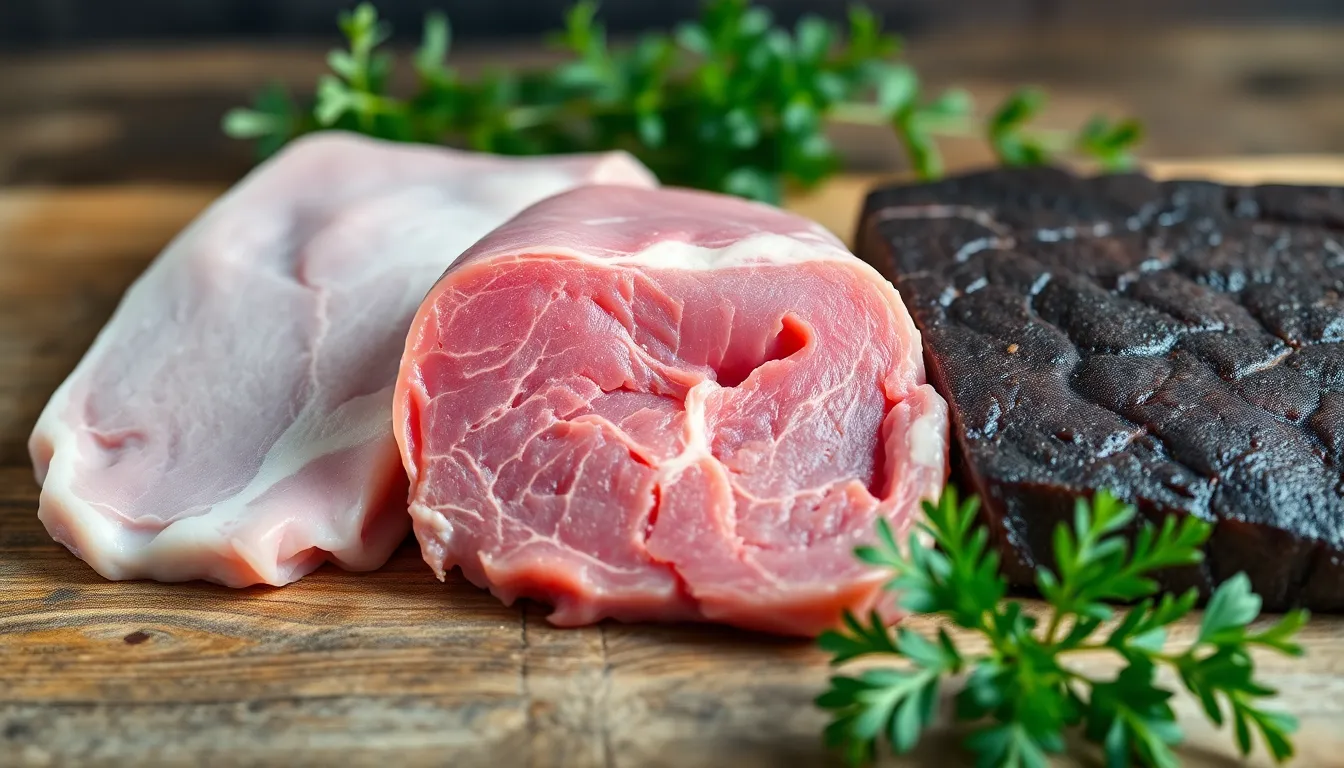

Veal comes in various types, each reflecting different raising methods and diets of the calves. Understanding these types helps in appreciating the flavors and textures of veal.
Milk-Fed Veal
Milk-fed veal is sourced from calves primarily raised on a liquid diet of milk or milk replacer. This diet leads to a pale pink color and a delicate texture, often prized in gourmet circles. Typically, these calves are around 5 to 6 months old at slaughter, resulting in tender meat. The flavor profile remains mild, making it ideal for dishes where the veal’s subtle taste can shine through. Chefs commonly use milk-fed veal in recipes such as veal piccata or creamy veal sauces.
Grain-Fed Veal
Grain-fed veal consists of calves that consume a diet rich in grains and sometimes forage. This approach enhances the meat’s color, giving it a deeper pink hue and a more robust flavor compared to milk-fed variations. Generally, these calves are around 6 to 8 months old when processed, contributing to a firmer texture. Grain-fed veal is versatile and works well in hearty dishes like veal stew or roasted cuts. The increased marbling due to the grain diet also adds to the overall richness of the meat.
Pasture-Raised Veal
Pasture-raised veal comes from calves that graze on open pastures, allowing them natural access to grass and forage. This method emphasizes animal welfare and produces meat with a rich flavor due to the diverse diet. Typically, these calves are slightly older, often around 8 to 12 months. The meat displays a darker color and firmer texture, appealing to those seeking a more robust veal experience. Chefs might choose pasture-raised veal for grilled dishes or braised preparations, emphasizing its complex, earthy flavors.
Nutritional Profile of Veal
Veal offers a rich nutritional profile that appeals to health-conscious consumers and culinary enthusiasts alike. This section explores its protein content along with essential vitamins and minerals.
Protein Content
Protein serves as a primary component of veal, boasting around 27 grams per 100 grams. This high protein content supports muscle growth and repair, making veal a suitable choice for those seeking to enhance their diet. Lean cuts provide a low-fat option, maintaining flavor without excess calories. In comparison to other meats, veal’s protein density stands out, making it an excellent addition to various meal plans. Athletes and active individuals often seek out veal for its quality protein, which aids in recovery and performance.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals found in veal contribute significantly to its nutritional benefits. Vitamin B12, crucial for nerve function and the production of red blood cells, is present in substantial amounts. Iron content reaches approximately 2.6 milligrams per 100 grams, promoting healthy blood circulation. Zinc, which supports immune health, can also be found in veal, enhancing the body’s ability to fend off illnesses. Among other nutrients, niacin and riboflavin offer energy production benefits, making veal a well-rounded protein source that bolsters overall health.
Ethical Considerations
Concerns surrounding the production of veal often focus on ethical animal treatment and sustainability practices. Animal welfare remains a significant issue in veal production.
Animal Welfare Concerns
Many critics argue that traditional veal farming methods compromise calf welfare. Practices like raising calves in individual pens can lead to physical and psychological distress. Group housing often provides a more humane environment, allowing social interaction among calves. Advocates for animal rights emphasize the importance of humane treatment in every stage of life, from birth until harvest. Certification programs, such as Certified Humane and Animal Welfare Approved, help consumers identify ethical sources for veal.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices play a crucial role in modern veal production. Producers increasingly adopt pasture-raised methods, allowing calves to graze on natural forage. This approach not only enhances calf welfare but also improves meat quality. Additionally, sustainable farms often employ rotational grazing, which benefits soil health and reduces environmental impact. Consumers increasingly seek out veal from these ethical sources, driving a shift toward more responsible farming practices. Implementing sustainable measures helps ensure that veal production supports both animal welfare and environmental stewardship.
Culinary Uses of Veal
Veal serves as a versatile ingredient in various cuisines, offering unique flavors and textures. Chefs prize its tenderness and mild taste, making it suitable for numerous preparations.
Popular Dishes
Several popular dishes feature veal prominently. Veal osso buco, a classic Italian dish, combines slow-cooked veal shanks with vegetables and broth, resulting in rich flavors. Veal scaloppine, featuring thinly sliced meat sautéed in a lemon-butter sauce, provides a quick yet elegant meal. In France, veal blanquette consists of a creamy stew paired with mushrooms and carrots. Additionally, veal Milanese, which involves breading and frying, evokes a satisfying crunch with every bite. These examples highlight the culinary versatility of veal across global cuisines.
Cooking Techniques
Various cooking techniques enhance the flavors of veal. Braising allows the meat to become tender while absorbing the essence of accompanying ingredients. Grilling adds a smoky char, enhancing the natural taste of the meat. Sautéing provides a quick cooking option, ensuring the meat remains juicy. Roasting brings out the richness of larger cuts like leg or shoulder, creating a flavorful crust. Each technique contributes to the dish’s overall profile, allowing chefs to showcase veal’s distinct qualities.
Veal stands out as a unique ingredient that brings both flavor and versatility to the culinary world. Its various types reflect the methods of production and the diets of the calves, allowing chefs to create diverse dishes that cater to different tastes. The nutritional benefits of veal, along with its rich protein content, make it an appealing choice for health-conscious individuals.
As ethical considerations continue to shape consumer preferences, the shift towards responsible farming practices highlights the importance of animal welfare in veal production. Understanding these aspects not only enriches one’s appreciation of veal but also encourages informed choices in the kitchen. Embracing this delicacy can lead to delightful culinary experiences that celebrate both tradition and innovation.